COM_MIC_TEXT_TITLE
Abstract
Entropy(S,熵), an extensive property of a thermodynamic system, can be describe by formula as below,
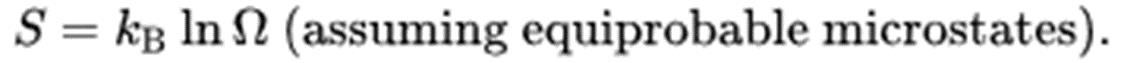
Entropy equals the natural logarithm of the number of microstates (Ω), multiplied by the Boltzmann constant kB.
Researches about heart rate variability (HRV) focused on clinical situations such as: AMI, CHF, diabetic neuropathy, depression, post-cardiac transplant, susceptibility to SIDS, cirrhosis, sepsis, and poor survival in premature babies. The methods used for HRV include: time domain analysis, frequency domain analysis, geometric methods, non-linear methods, and long term correlations. HRV measures fluctuations in autonomic inputs to the heart rather than the mean level of autonomic inputs. Entropy of heart rate is applied to predict the outcome of critical patients. Other researches applied entropy to analyze EEG about nociceptive responsiveness levels during sedation-analgesia. Many kinds of entropy calculations were developed. Each method has trade-offs relating to accuracy, linearity, and processing time.
Cardiac output equals heart rate times stroke volume. The correct evaluation of stroke volume depends on images. Recently, noninvasive continuous cardiac output monitoring was developed using infrared technology. However, it remains an estimation of cardiac output. Physicians usually evaluate patient’s cardiovascular conditions in four dimensions: preload, afterload, rhythm, and contractility. Here we propose to use entropy to evaluate cardiac output fluctuations by using noninvasive continuous cardiac output monitoring.